Recent Changes that Impact Wood Packaging Material
The penalties for non-compliant ISPM 15 wood packaging materials (WPM) are a serious matter to take into consideration when selecting components for the design of a unit load. Besides penalty costs, the end user will require a duplicate shipment if customs liquidates the product held up instead of denying entry. With customer delivery late fees becoming a common business occurrence as well, the actual cost of saving a few cents on some pallets could become a costly mistake in the long-term.
WPM is a key component for the transportation and handling of unit loads throughout supply chains in today’s global market. The objects classified as WPM are pallets, skids, crates, bracing, dunnage, and wood components that are thicker than 0.24 in. (6 mm). The shipment and treatment of these items across any major country’s border have been regulated due to the negative impact on forests, from the migration of several insect species across the globe.
These regulations require that the WPM have less than a 1.18 in. (3 cm) width of bark and have been heat treated when it leaves its country of manufacture, if a third of the WPM is remanufactured the pallet must be treated again. This heat treatment must bring the wood’s internal temperature up to a minimum of 132.80⁰F (56⁰C) for a minimum time of 30 minutes. However, there are several global exclusions to this mandatory requirement. These exemptions are:
- WPM made from “processed wood”, such as Litco’ s Engineered Molded Wood™ pallets and core plugs, that have been created using heat, glue, and pressure
- Barrels for wine and spirits that have been heated during their manufacture
- Sawdust, wood shavings, wood wool, and other fine wood particles
- Wood pieces permanently attached to freight containers and vehicles
The violations of International Standards for Phytosanitary Measures (ISPM) 15 are:
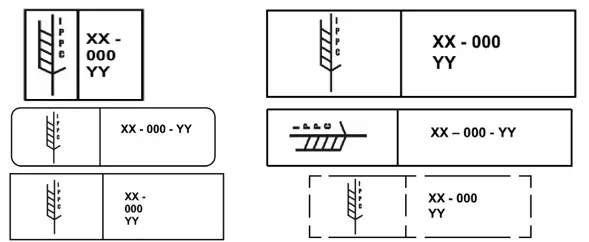
- Absent, unapproved, or incorrect application of International Plant Protection Convent (IPPC) markings/stamp outlined in ISPM 15 (see Figure 1)
- Pest Infested WPM
The penalties associated with non-compliant WPM have increased recently as of September 25, 2017 for a handful of countries. The exact pricing for these penalties varies based on the country into which the product is being shipped in to. The importers in violation can receive penalties based on the violations of fraud, gross negligence, and negligence. The countries that have provided information on the structure for their penalties and their amounts are as follows:
- Fraud: will not exceed the domestic value of the product
- Gross Negligence: the lesser of the two, four times the lawful duties, taxes, and fees or the domestic value of product
- Negligence: the lesser of the two, two times the lawful duties, taxes, and fees or the domestic value of product
The Litco Solution
The simplest way to avoid the potential of non-compliance, is by using Litco’s Engineered Molded Wood™ export-grade pallets (EMWP) and core plugs. They are a low cost solution for export shipper’s unit load needs. They are included under the ISPM 15 regulation exemptions. This is because the manufacturing processes of our EMWP uses a high-heat process which exceeds 350⁰F (during the molding. This renders them welcome, as is, into any trading member country. In addition, due to its exemption, does not require any additional heat treatment or IPPC stamping mark for export as per the examples above.
References
- International Plant Protection Convention (2017) International standards for phytosanitary measures: ISPM 15, Regulation of wood packaging material in international trade. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy.
- International Plant Protection Convention (2001) International standards for phytosanitary measures: ISPM 13, Guidelines for the notification of non-compliance and emergency action. Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, Rome, Italy.
- S. Customs and Border Protection (2004) Customs Administrative Enforcement Process: Fines, Penalties, Forfeitures and Liquidate Damages. U.S. Department of Homeland Security
- Animal and Plant Health Inspection Service (2017) Countries Requiring ISPM 15. United States Department of Agriculture.
Notes: Outlined in ISPM 15 on page 7 in section 2.1 the list of products exempt from the regulations can be found. Instances of non-compliance can be found on page 9 of ISPM 13 in section 4.1. On page 29 of the U.S. Customs and Border Protection document a general outline for the classification, type, and penalty amount for a violation/non-compliance and page 14 gives an overview of said infractions.








